B. Grégoire, X. Montero, M.C. Galetz, G. Bonnet, F. Pedraza
Corrosion Science 224 (2023), 111517, DOI: 10.1016/j.corsci.2023.111517
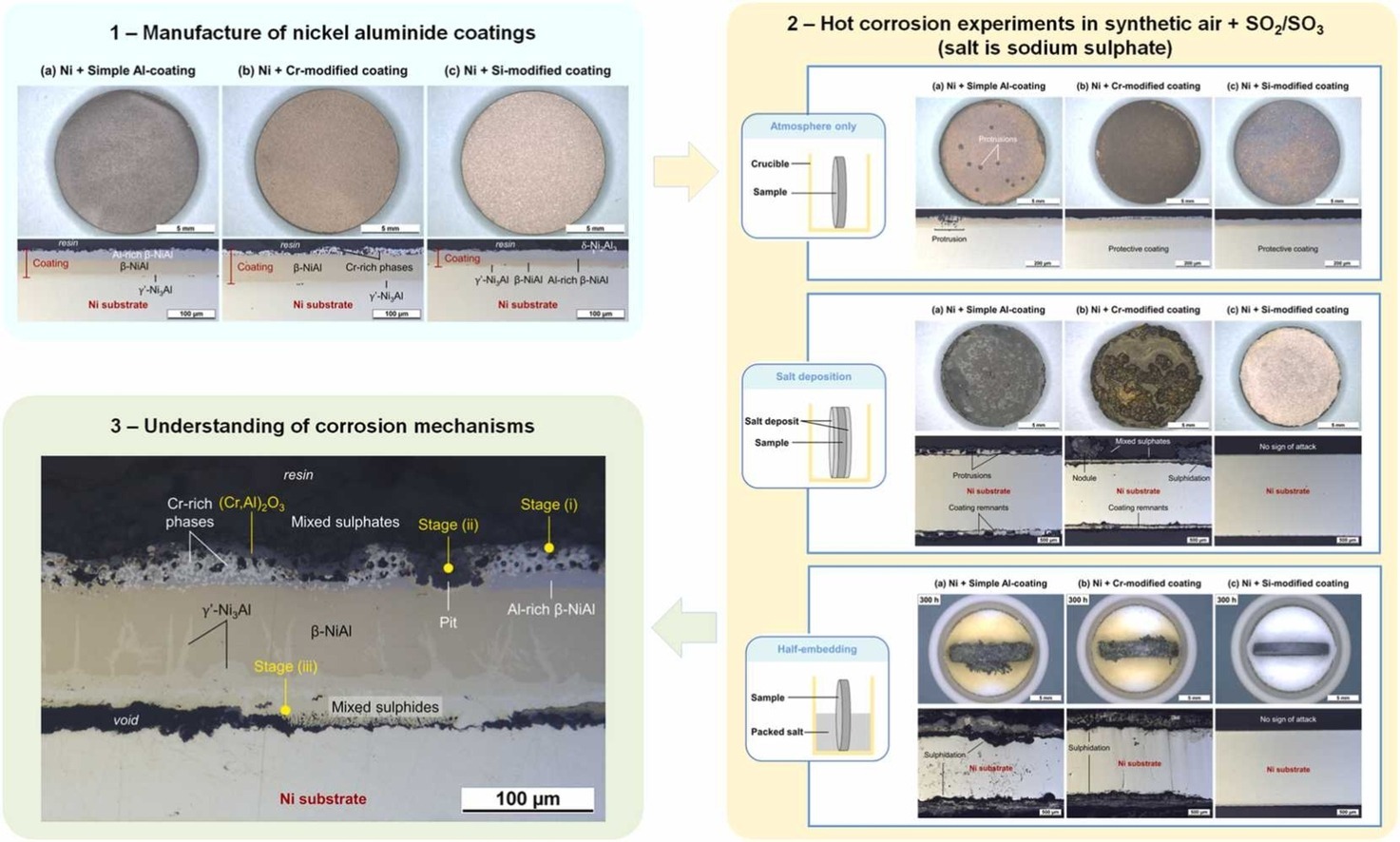
The effects of chromium and silicon modification on the microstructure and hot corrosion resistance of slurry aluminide coatings applied on pure nickel was studied by in-depth microscopic analyses. The simple and the Cr-modified aluminide coatings provided limited protection in Type II hot corrosion conditions but the Si-modified coating exhibited outstanding resistance with no sign of attack after 300 h of isothermal exposure at 700 °C. The synergistic dissolution between NiO and Al2O3/Cr2O3 appears responsible for the onset of the corrosion attack for the simple and Cr-modified coatings while silicon is shown to extend the incubation period.